Communicating with Web Services
You are looking at an older version of the documentation. The latest version is found here.
The Data Virtuality Server makes communicating with web services easy: you can use both RESTful and SOAP web services. Only one thing is required: a valid data source of type Web service. The web service data source provides two stored procedures for retrieving the data from the web service, as described below. When clicking in the Data Virtuality Studio to add a new data source, the dialogue for web services looks as follows:
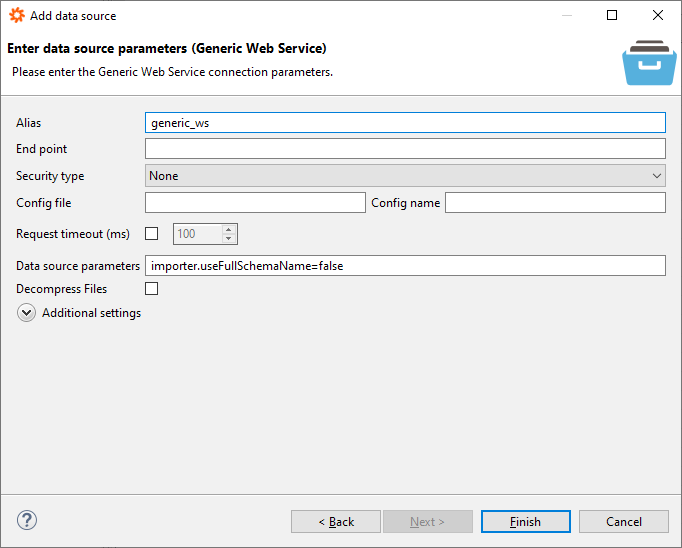
The only mandatory information is an alias for the data source. In the example above, the name ws is given. We can specify an endpoint, i.e., a web address, which can later be implicitly used for requests. The field can be empty, requiring you to always provide an endpoint when using the procedures. Leaving the field blank allows you to use one data source for all kinds of web service requests to different APIs. It is, of course, possible to create multiple data sources and use them in a logical manner assigned to different APIs.
It is also possible to specify a type of security. Note that if you choose a type of security (and the additional information you have to provide), this information will always be sent with each web request you cannot communicate with all APIs anymore. However, it might be required to set up OAuth2 for example, if an API strictly requires it.
Another useful option is the timeout setting which allows you to determine when the server should stop waiting for a response to your requests. Some web endpoints are slower, and slightly increasing the timeout can solve simple problems caused by the data reaching the server too late.
When the data source is added, we have the following two procedures:
- invoke(): used for SOAP requests (here ws.invoke)
- invokeHTTP(): used for REST requests (here ws.invokeHTTP)
REST Web Services (invokeHttp() Procedure)
Here are the input parameters and how to use them:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| The request action, usually one of the following: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE |
request | The data of the object which is sent to the API; null if data shall only be retrieved from the API |
endpoint | The web endpoint to where the request is sent; can be a full URL or only a suffix (it is appended to the data source's default endpoint). If null, the web service's default endpoint is used |
requestContentType | The data type of the object which is sent to the API; null if data shall only be retrieved from the API. Valid values are application/xml, application/json, text/plain, and application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
requestHeaders | Additional headers that are sent to the API, such as authorization headers |
failOnHTTPError | Enables you to ignore HTTP errors |
Sample Call
This simple REST request with the invokeHTTP() procedure includes only action and endpoint:
SELECT TO_chars(w.result,'UTF-8') FROM (
CALL generic_ws.invokeHTTP (
action =>'GET',
endpoint => 'https://academy.datavirtuality.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/forecast.json'
)
)w;;The results of the call to the web service can be further processed, for example, by using the TEXTTABLE, XMLTABLE, and JSONTOXML functions. This processing can be defined using XML/JSON or CSV wizard in the Data Virtuality Studio.
When passing parameters, use the QueryString function to build the URL. The example below builds the following URL: https://www.7timer.info/bin/astro.php?lon=113.2&lat=23.1&ac=0&unit=metric&output=json&tzshift=0:
SELECT TO_chars(w.result,'UTF-8') FROM (
CALL generic_ws.invokeHTTP (
action =>'GET',
endpoint => QueryString(
'https://www.7timer.info/bin/astro.php',
113.2 AS lon,
23.1 AS lat,
0 AS ac,
'metric' AS unit,
'json' AS "output",
0 AS tzshift
)
)
)w;;SOAP Web Services (invoke() Procedure)
Here are the input parameters and how to use them:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
action | The request action; usually GET or POST |
binding | The web service binding, can be one of the following: HTTP, SOAP11, SOAP12 |
request | The actual XML request according to SOAP standards |
endpoint | The web endpoint to where the request is sent; can be a full URL or only a suffix (it is appended to the data source's default endpoint). If null, the web service's default endpoint is used |
An easy way to get sample requests for a given SOAP web service is to use the tool SoapUI which only needs a valid WSDL location (local or web) and it can generate request templates. A good sample is the WSDL Schema file from https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/
Sample Call
The following SOAP request with the invoke() procedure creates a SOAP call to request the capital of Germany. It uses HTTP as binding, POST as action, and an XML request generated by the SoapUI. Otherwise one has to manually browse through the WSDL file and build the XML with the information given by it:
SELECT "w.result"
FROM (
EXEC "generic_ws".invoke(
"binding" => 'HTTP',
"action" => 'POST',
"request" => '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<CapitalCity xmlns="http://www.oorsprong.org/websamples.countryinfo">
<sCountryISOCode>DE</sCountryISOCode>
</CapitalCity>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
',
"endpoint" => 'http://webservices.oorsprong.org/websamples.countryinfo/CountryInfoService.wso'
)
) AS w;;Sample Result
<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<m:CapitalCityResponse xmlns:m="http://www.oorsprong.org/websamples.countryinfo">
<m:CapitalCityResult>Berlin</m:CapitalCityResult>
</m:CapitalCityResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>See Also
Facebook: Handle Paged Results for a guide on how to work with paged results
