Google BigQuery
Type Name
bigquery
Connection Properties
Template name: bigquery
Appropriate translator name: bigquery
Properties:
projectId(required)transformQuery(default:TRUE); (obsolete)credentialFactory(default:com.datavirtuality.dv.core.oauth.credential.BigQueryOAuthCredentialFactory)allowLargeResults (obsolete)largeResultsDefaultDatasettableMaxResultsfetchSizerefreshTokenaccessTokenexpirationTimeMillisecondsregionauthCoderedirectUriuser-name(required)password(a path to a key file or a Base64 string presentation of the key file; see note below)ClientIdClientSecretdriver(default:bigquery)driver-class(default:com.datavirtuality.jdbc.bq.BQDriver)storageProjectId(default: empty)storageUser(default: empty)storagePassword(default: empty)new-connection-sqlcheck-valid-connection-sql(default:select 1)min-pool-size(default:2)max-pool-size(default:70)readTimeout(default:20000,0for an infinite, a negative for the default)connectTimeout(default:20000,0for an infinite, a negative for the default)
The password property is stored in the SYSADMIN.Connections table as a Base64 string, even when set as a path to a key file. In the import script, it will also be presented as a Base64 string, therefore the key file does not need to be backed up for migration.
The password property supports Base64 string values since v25.3
Example
CALL SYSADMIN.createConnection('bq2','bigquery','projectId=XXXX,user-name=XXXX@developer.gserviceaccount.com,password=$${jboss.server.config.dir}/../deployments/bigquery.p12') ;;
CALL SYSADMIN.createDatasource('bq2','bigquery','importer.useFullSchemaName=false,importer.useCatalogName=false','supportsNativeQueries=true,uploadMode=CLOUDSTORAGE,bucketName=dv_upload_bucket,useDdl=false') ;;It is highly recommended to specify a bucketName when creating a BigQuery data source because of the following:
a bucket creation limit that can be exceeded while performing multiple data inserts. Please refer to the Google Cloud Storage documentation for detailed information;
region mismatch between a BigQuery data set and a temporary bucket which may cause errors while inserting data. Please, refer to the Google BigQuery documentation for more details.
Translator Properties
Translator Properties Shared by All JDBC Connectors
(Properties listed in alphabetical order)
To view the full table, click the expand button in its top right corner
Name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Sets a template to convert Examples
SQL
|
|
| Database time zone, used when fetching date, time, or timestamp values | System default time zone |
| Specific database version, used to fine-tune pushdown support | Automatically detected by the server through the data source JDBC driver, if possible |
| Only considered when |
|
| If |
|
| Maximum size of prepared insert batch |
|
| Sets a template to convert Examples
SQL
|
|
| If |
|
| Forces a translator to issue a Example
SQL
|
|
| If If |
|
| If If |
|
| If |
|
| if |
|
| Embeds a / comment / leading comment with session/request id in the source SQL query for informational purposes |
|
The names of the translator properties are case-sensitive.
Translator Properties Specific for Google BigQuery
To view the full table, click the expand button in its top right corner
Name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| String property. If set, the translator replaces all null characters in strings before executing | Single space |
| Values:
|
|
| Value: bucket name Only for the default ( | |
| Value: bucket prefix Only for the default ( | |
| Value: name of a folder in a bucket Only for the default ( | |
| Value: boolean If |
|
| If set to If set to |
|
Data Source Properties
Data Source Properties Shared by All JDBC Connectors
(Properties listed in alphabetical order)
To view the full table, click the expand button in its top right corner
Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Replaces |
|
| Database catalogs to use. Can be used if the Only for Microsoft SQL Server and Snowflake:
Only for Snowflake: the | Exasol:
SQL
All others: empty |
|
| |
|
Please note that writing into a data source is only possible if this parameter is set. | Empty |
| Turns on metadata cache for a single data source even when the global option is turned off. Together with |
|
| Case-insensitive regular expression that will exclude a matching fully qualified procedure name from import | Empty |
| Comma-separated list of schemas (no | Oracle:
SQL
All others: empty |
| Case-insensitive regular expression that will exclude a matching fully qualified table name from import. Does not speed up metadata loading. Here are some examples: 1. Excluding all tables in the (source) schemas
SQL
2. Excluding all tables except the ones starting with "public.br" and "public.mk" using a negative lookahead:
SQL
3. Excluding "tablename11" from the list ["tablename1", "tablename11", "company", "companies"]:
SQL
| Empty |
| Fetch size assigned to a resultset on loading metadata | No default value |
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to Please note that it is currently not possible to import procedures which use the same name for more than one parameter (e.g. same name for |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| Procedure(s) to import. If omitted, all procedures will be imported. | Empty |
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
| Schema(s) to import. If omitted or has "" value, all schemas will be imported. Schema names can be fully qualifed, for example | Empty |
| If set to |
|
| Table(s) to import. If omitted, all tables will be imported. Table names can be fully qualifed, for example | Empty |
| Comma-separated list (without spaces) of table types to import. Available types depend on the DBMS. Usual format: Other typical types are | Empty |
| If set to |
|
| If set to Please note that this may lead to objects with duplicate names when importing from multiple schemas, which results in an exception |
|
| If set to |
|
| If set to |
|
The names of the data source properties are case-sensitive.
importer.catalog property can be used in Snowflake together with the db connection property since v25.3
importer.schemaPattern supports fully qualified names since v25.3
importer.tableNamePattern supports fully qualified names since v25.3
Creating/Dropping Tables and Inserting Data
In order to create/drop tables and insert data into a BigQeury data source, the importer.defaultSchema data source property should be set to the name of the target dataset. Here is an example:
CALL SYSADMIN.createConnection(name => 'bq', jbossCliTemplateName => 'bigquery', connectionOrResourceAdapterProperties => 'projectId=XXXX,user-name=XXXX-ZZZZ@developer.gserviceaccount.com,password=PATH_TO_KEY_FILE') ;;
CALL SYSADMIN.createDatasource(name => 'bq', translator => 'bigquery', modelProperties => 'importer.useCatalogName=false,importer.defaultSchema=TARGET_DATA_SET,importer.schemaPattern=SCHEMA_PATTERN_INCLUDING_TARGET_DATASET,importer.useFullSchemaName=false') ;;Segmenting with Partitioned Tables
The BigQuery partitioning functionality is supported in both API and DDL (useDdl=TRUE) modes.
Partitioning is supported via the OPTIONS clause.
Types of Partitioning
Integer range partitioning
You can partition a table based on ranges of values in a specific INTEGER column.
Time-unit column partitioning
You can partition a table on a DATE or TIMESTAMP column in the table.
For the TIMESTAMP column, the partitions can have either hourly, daily, monthly, or yearly granularity. For DATE columns, the partitions can have daily, monthly, or yearly granularity. Partitions boundaries are based on UTC time.
Ingestion time partitioning
Valid only for DDL mode.
An ingestion-time partitioned table has a pseudocolumn named _PARTITIONTIME. The value of this column is the ingestion time for each row, truncated to the partition boundary (such as hourly or daily). Instead of using _PARTITIONTIME, you can also use _PARTITIONDATE. The _PARTITIONDATE pseudocolumn contains the UTC date corresponding to the value in the _PARTITIONTIME pseudocolumn.
You can choose hourly, daily, monthly, or yearly granularity for the partitions.
Partitioning Options
partition_expiration_days
When you create a table partitioned by ingestion time or time-unit column, you can specify a partition expiration. This setting specifies how long BigQuery keeps the data in each partition. The setting applies to all partitions in the table, but is calculated independently for each partition based on the partition time.
Accepts FLOAT values.
require_partition_filter
Specifies whether queries on this table must include a a predicate filter that filters on the partitioning column. The default value is FALSE.
partition_expression
Partition_expression is an expression that determines how to partition the table. The partition expression can contain the following values:
| description | partitioning type | valid for mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partition by ingestion time with daily partitions | Ingestion time | DDL |
| Equivalent to | Ingestion time | DDL |
| Partition by the | Time-unit column | API/DDL |
| Partition by the | Time-unit column | API/DDL |
| Partition by the | Time-unit column | API/DDL |
| Partition by the | Time-unit column | DDL |
| Partition by ingestion time with the specified partitioning type | Ingestion time | DDL |
| Partition by the | Time-unit column | API/DDL |
| Partition by an integer column with the specified range, where:
| Integer range | API/DDL |
Examples
Partitioning by the
DATEcolumn with daily granularity, keeping data for 3 days in partition and required filter that filters on the partitioning column for querying from table which means that the select query should contains where clause with DATE column:
CREATE TABLE bigquery.partition1 (i INTEGER, d DATE, s STRING) OPTIONS (partition_by 'd',partition_expiration_days '3', require_partition_filter 'true') ;;Creating a table partitioned on a timestamp range with monthly granularity:
CREATE TABLE bigquery_ddl.partition_ddl_date (i integer, d timestamp, s string) OPTIONS (partition_by 'DATE_TRUNC(d, MONTH)') ;;Creating a table partitioned on integer range required filter that filters on the partitioning column for querying from table which means that the
SELECTquery should contains where clause with theINTEGERcolumn:
CREATE TABLE bigquery_ddl.partition_ddl_integer (i integer, d timestamp, s string) OPTIONS (partition_by 'RANGE_BUCKET(i, GENERATE_ARRAY(0, 100, 10))', require_partition_filter 'true') ;;Partitioning options and integer-range, date-unit partitioning for API mode are available since v4.10
Clustering
Clustering is supported via the OPTIONS clause:
CREATE TABLE bigquery.cluster (i integer, d date, ts timestamp, s string, b boolean) OPTIONS (cluster_by 'i,d,ts,s') ;;Partitioning and Clustering for Materialization of Recommended Optimizations
Materialized tables in BigQuery can be partitioned and clustered using the SYSADMIN.createCreationParam procedure.
Parameter keys:
partition_bycluster_bypartition_expiration_daysrequire_partition_filter
Example
-- Add "partition_by" creation parameter
CALL "SYSADMIN.createCreationParam"(
"recOptId" => 1,
"paramKey" => 'partition_by',
"paramValue" => 'RANGE_BUCKET(i, GENERATE_ARRAY(0, 100, 10))'
);;
-- Add "require_partition_filter" creation parameter
CALL "SYSADMIN.createCreationParam"(
"recOptId" => 1,
"paramKey" => 'require_partition_filter',
"paramValue" => true
);;For the recommended optimization with an ID equal to 1 a materialized table will be created with partitioning as in the following example:
CREATE TABLE bigquery_ddl.partition_ddl_integer (i integer, d timestamp, s string) OPTIONS (partition_by 'RANGE_BUCKET(i, GENERATE_ARRAY(0, 100, 10))', require_partition_filter 'true') ;;Configuring 3-legged OAuth for BigQuery
To set up 3-legged OAuth with BigQuery, follow these steps:
Log in to the Developer Console for your BigQuery project.
Generate new OAuth2 credentials (a pair of
CLIENT_IDandCLIENT_SECRETkeys).
Substitute
CLIENT_IDin the link below with yourCLIENT_IDand follow this link in the browser:
Choose 'Allow' to provide access:
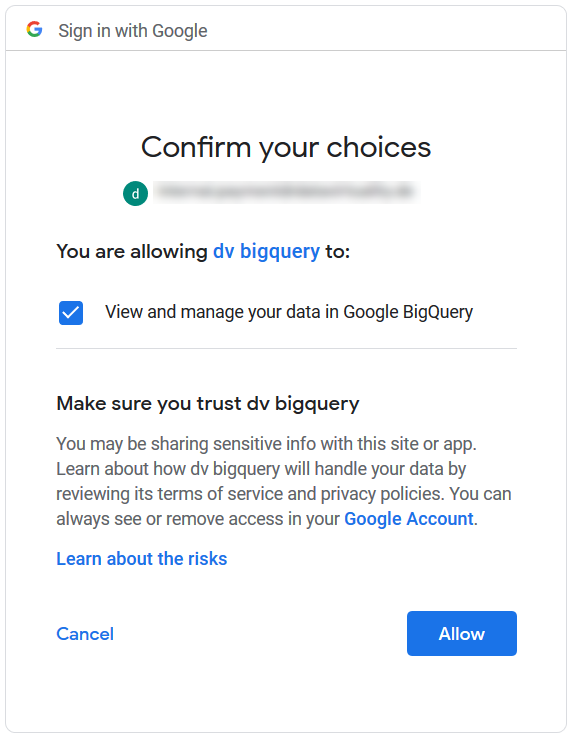
You will be redirected to a non-existent page, which is correct. Copy the page URL to obtain the code:
![]() The OAuth code is only valid for 10 minutes
The OAuth code is only valid for 10 minutes
|
Create a data source using the
CLIENT_IDandCLIENT_SECRETobtained in step 3,AUTH_CODEobtained in step 5, andPROJECT_IDof your BigQuery project. TheredirectUrlshould be the same as in steps 3 and 5:
CALL SYSADMIN.createConnection('bq3legged','bigquery','authType=OAUTH,
projectId=PROJECT_ID ,
authCode=AUTH_CODE ,
redirectUri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A9000%2Fredirect.html%3Fto%3Dconnect/bigquery/oauth,
user-name=CLIENT_ID,
password=CLIENT_SECRET') ;;
CALL SYSADMIN.createDatasource('bq3legged','bigquery','importer.schemaPattern=bq_schema_pattern,importer.defaultSchema=bq_schema,
importer.useFullSchemaName=false,importer.useCatalogName=false','supportsNativeQueries=true') ;;See Also
Partitioning Tables in BigQuery to learn how to convert a non-partitioned table into a partitioned one for improved query performance
